设计模式之外观模式
定义
外观模式:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个统一的入口。外观模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
了解
外观模式是一种使用频率非常高的结构型设计模式,它通过引入一个外观角色来简化客户端与子系统之间的交互,为复杂的子系统调用提供一个统一的入口,降低子系统与客户端的耦合度,且客户端调用非常方便。
一个客户类需要和多个业务类交互,而这些需要交互的业务类经常会作为一个整体出现,由于涉及到的类比较多,导致使用时代码较为复杂,此时,特别需要一个类似服务员一样的角色,由它来负责和多个业务类进行交互,而客户类只需与该类交互。外观模式通过引入一个新的外观类(Facade)来实现该功能,外观类充当了软件系统中的“服务员”,它为多个业务类的调用提供了一个统一的入口,简化了类与类之间的交互。在外观模式中,那些需要交互的业务类被称为子系统(Subsystem)。如果没有外观类,那么每个客户类需要和多个子系统之间进行复杂的交互,系统的耦合度将很大;而引入外观类之后,客户类只需要直接与外观类交互,客户类与子系统之间原有的复杂引用关系由外观类来实现,从而降低了系统的耦合度. 栗子:
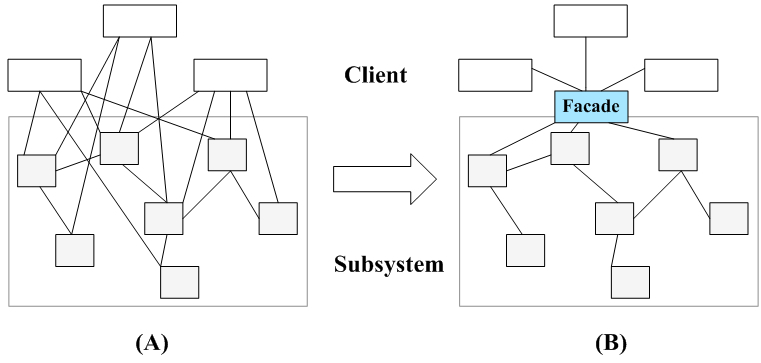
结构图
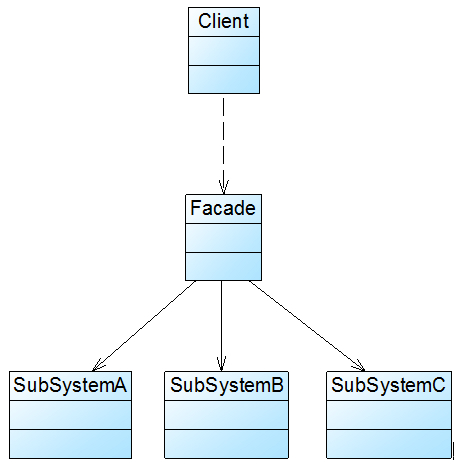
Facade(外观角色):在客户端可以调用它的方法,在外观角色中可以知道相关的(一个或者多个)子系统的功能和责任;在正常情况下,它将所有从客户端发来的请求委派到相应的子系统去,传递给相应的子系统对象处理。
SubSystem(子系统角色):在软件系统中可以有一个或者多个子系统角色,每一个子系统可以不是一个单独的类,而是一个类的集合,它实现子系统的功能;每一个子系统都可以被客户端直接调用,或者被外观角色调用,它处理由外观类传过来的请求;子系统并不知道外观的存在,对于子系统而言,外观角色仅仅是另外一个客户端而已。
典型代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class SubSystemA
{
public void MethodA()
{
}
}
class SubSystemB
{
public void MethodB()
{
}
}
class SubSystemC
{
public void MethodC()
{
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Facade
{
private SubSystemA obj1 = new SubSystemA();
private SubSystemB obj2 = new SubSystemB();
private SubSystemC obj3 = new SubSystemC();
public void Method()
{
obj1.MethodA();
obj2.MethodB();
obj3.MethodC();
}
}
|
// 客户类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.Method();
}
}
|
示例
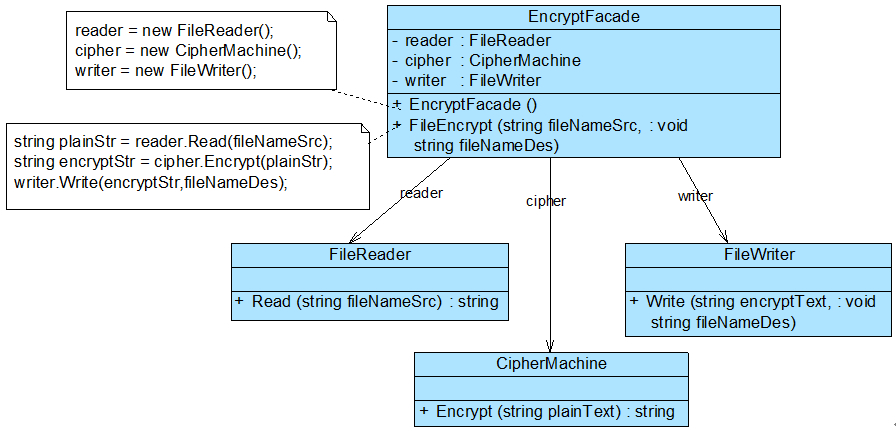
抽象外观类
在标准的外观模式结构图中,如果需要增加、删除或更换与外观类交互的子系统类,必须修改外观类或客户端的源代码,这将违背开闭原则,因此可以通过引入抽象外观类来对系统进行改进,在一定程度上可以解决该问题。在引入抽象外观类之后,客户端可以针对抽象外观类进行编程,对于新的业务需求,不需要修改原有外观类,而对应增加一个新的具体外观类,由新的具体外观类来关联新的子系统对象,同时通过修改配置文件来达到不修改任何源代码并更换外观类的目的。
如果不增加新的外观类,只能通过修改原有外观类Facade的源代码来实现加密类的更换,将原有的对CipherMachine类型对象的引用改为对NewCipherMachine类型对象的引用,这违背了开闭原则,因此需要通过增加新的外观类来实现对子系统对象引用的改变。
如果增加一个新的外观类NewFacade来与FileReader类、FileWriter类以及新增加的NewCipherMachine类进行交互,虽然原有系统类库无须做任何修改,但是因为客户端代码中原来针对Facade类进行编程,现在需要改为NewFacade类,因此需要修改客户端源代码。因此引入一个抽象外观类,客户端针对抽象外观类编程,而在运行时再确定具体外观类。栗子:

原有外观类Facade也需作为抽象外观类AbstractFacade类的子类,更换具体外观类时只需修改配置文件,无须修改源代码,符合开闭原则。具体见下面撸的代码!!!
总结
外观模式是一种使用频率非常高的设计模式,它通过引入一个外观角色来简化客户端与子系统之间的交互,为复杂的子系统调用提供一个统一的入口,使子系统与客户端的耦合度降低,且客户端调用非常方便。外观模式并不给系统增加任何新功能,它仅仅是简化调用接口。在几乎所有的软件中都能够找到外观模式的应用,如绝大多数B/S系统都有一个首页或者导航页面,大部分C/S系统都提供了菜单或者工具栏,在这里,首页和导航页面就是B/S系统的外观角色,而菜单和工具栏就是C/S系统的外观角色,通过它们用户可以快速访问子系统,降低了系统的复杂程度。所有涉及到与多个业务对象交互的场景都可以考虑使用外观模式进行重构。
优点
- 它对客户端屏蔽了子系统组件,减少了客户端所需处理的对象数目,并使得子系统使用起来更加容易。通过引入外观模式,客户端代码将变得很简单,与之关联的对象也很少。
- 它实现了子系统与客户端之间的松耦合关系,这使得子系统的变化不会影响到调用它的客户端,只需要调整外观类即可。
- 一个子系统的修改对其他子系统没有任何影响,而且子系统内部变化也不会影响到外观对象。
缺点
- 不能很好地限制客户端直接使用子系统类,如果对客户端访问子系统类做太多的限制则减少了可变性和灵活性。
- 如果设计不当,增加新的子系统可能需要修改外观类的源代码,违背了开闭原则。
适用场景
当要为访问一系列复杂的子系统提供一个简单入口时可以使用外观模式。
客户端程序与多个子系统之间存在很大的依赖性(引入外观类可以将子系统与客户端解耦,从而提高子系统的独立性和可移植性)。
层次化结构(可以使用外观模式定义系统中每一层的入口,层与层之间不直接产生联系,而通过外观类建立联系,降低层之间的耦合度)。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractFacade facade = new NewFacade();
facade.method("a.txt", "b.txt");
System.out.println("all is well!");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public interface AbstractFacade {
void method(String srcPath, String descPath);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public class Facade implements AbstractFacade {
private FileReader fileReader;
private CipherMachine cipherMachine;
private FileWriter fileWriter;
public Facade() {
this.fileReader = new FileReader();
this.cipherMachine = new CipherMachine();
this.fileWriter = new FileWriter();
}
@Override
public void method(String srcPath, String descPath) {
System.out.println("通过外观类调用各个具体子类业务系统>>>");
String read = this.fileReader.read(srcPath);
String encrypt = this.cipherMachine.encrypt(read);
this.fileWriter.writeFile(descPath, encrypt);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public class NewFacade implements AbstractFacade {
private FileReader fileReader;
private NewCipherMachine cipherMachine;
private FileWriter fileWriter;
public NewFacade() {
this.fileReader = new FileReader();
this.cipherMachine = new NewCipherMachine();
this.fileWriter = new FileWriter();
}
@Override
public void method(String srcPath, String descPath) {
System.out.println("通过外观类调用各个具体子类业务系统>>>");
String read = this.fileReader.read(srcPath);
String encrypt = this.cipherMachine.encrypt(read);
this.fileWriter.writeFile(descPath, encrypt);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
|
public class CipherMachine {
public String encrypt(String plainText)
{
System.out.println("数据加密,将明文转换为密文:");
String es = "";
char[] chars = plainText.toCharArray();
for (char aChar : chars) {
String c = String.valueOf(aChar % 7);
es += c;
}
System.out.println(es);
return es;
}
}
public class NewCipherMachine {
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
System.out.println("数据加密,将明文转换为密文:");
String es = "";
int key = 10;
char[] chars = plainText.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chars) {
int temp = Integer.valueOf(ch);
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
temp += key % 26;
if (temp > 122) {
temp -= 26;
}
if (temp < 97) {
temp += 26;
}
}
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
temp += key % 26;
if (temp > 90) {
temp -= 26;
}
if (temp < 65) {
temp += 26;
}
}
es += String.valueOf((char)temp);
}
System.out.println(es);
return es;
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class FileReader {
public String read(String filepath) {
try {
File file = new File(filepath);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
long filelength = file.length();
byte[] bb = new byte[(int) filelength];
fis.read(bb);
fis.close();
System.out.println("读取文件成功!加密前明文: " + new String(bb));
return new String(bb);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class FileWriter {
public void writeFile(String path, String txt) {
File file = new File(path);
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = txt.getBytes();
output.write(bytes);
output.close();
System.out.println("成功将加密数据写入目标文档!");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("将加密数据写入目标文档失败!");
}
}
}
|
相关资料
https://blog.csdn.net/lovelion/article/details/8258121
https://blog.csdn.net/lovelion/article/details/8259705
https://blog.csdn.net/lovelion/article/details/8259789



